理想中的代码
概览
一直在写代码,什么是理想中的代码
关于MVC
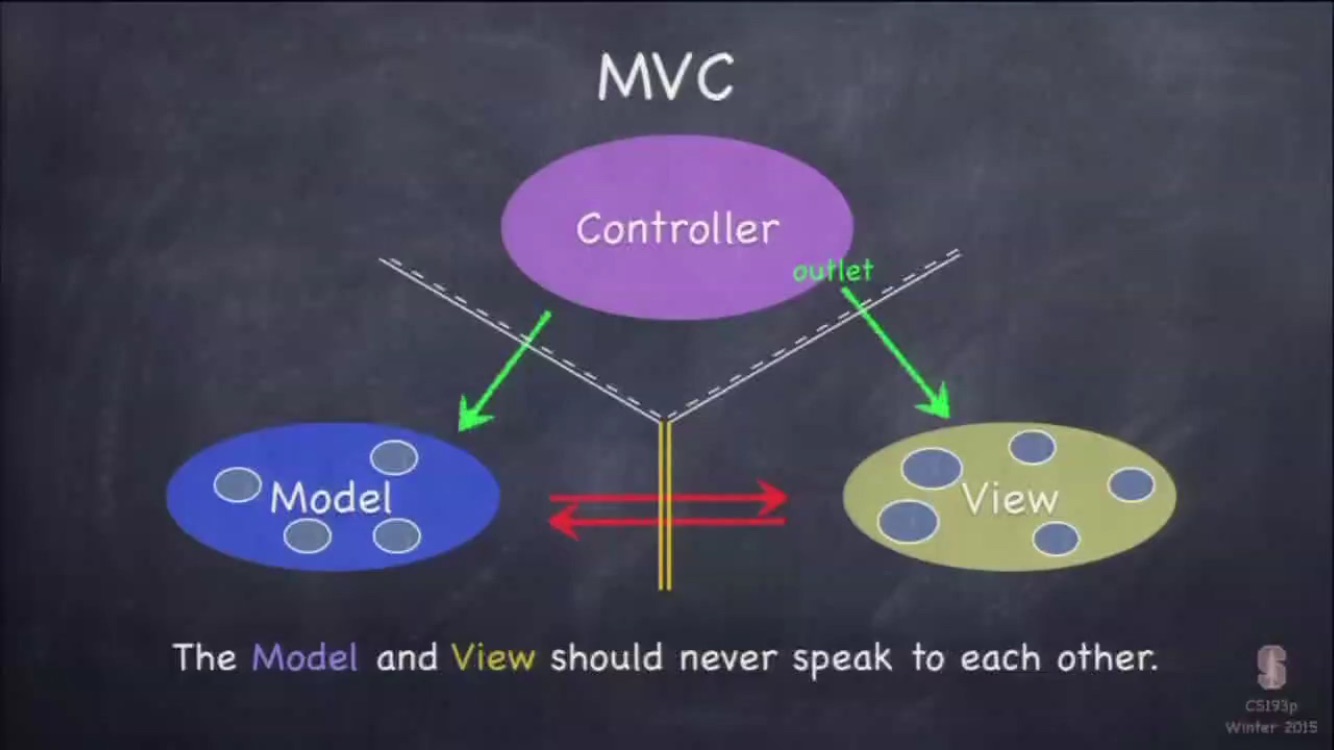
图片是《斯坦福大学公开课:iOS7应用开发》中第一节课中的图片,讲述了三者之间的关系。按照交通规则来看,黄色是不可逾越的,也就是说model和view之间不可以存在任何联系,controller可以访问和持有model和view,反之则不行。
那么问题来了,UICollectionViewCell,UITableViewCell属于什么呢?当然属于View,继承自它们的当然也属于View,为了方便,我们常常在某个cell中绑定一个model,然后在类里面根据model修改各个元素的值,我个人是不提倡这么做的。从单个页面来看,通常很便捷,但是从上面的图片来看,它已经违反了交通规则。
1、从单元测试来讲,提高了测试的耦合性,想要测试一个view必须先创建一个model
2、一旦绑定了一个类型的model将很难复用到其他界面相似的view,例如中国版的点赞列表、附近的人的列表、消息里面的关注列表,三者界面类似,数据model都是从user继承而来,又稍有不同,换句话说,需求可能是界面都不动,界面中的某个lable的text需要改变。另外如果一个view想要给其他业务或者其他团队或者开源出来给其他人用必须把model从cell中拿掉。这里可以举个开源的例子,com中聊天引用的一个项目JSQMessagesViewController 中的JSQMessagesCollectionViewCell
enum 枚举
enum Rank: Int {
case ace = 1
case two, three, four, five, six, seven, eight, nine, ten
case jack, queen, king
func simpleDescription() -> String {
switch self {
case .ace:
return "ace"
case .jack:
return "jack"
case .queen:
return "queen"
case .king:
return "king"
default:
return String(self.rawValue)
}
}
}
let ace = Rank.ace
let aceRawValue = ace.rawValue最初以为swift中的枚举只有以上添加了函数的操作,其实不然啊 看下面
/**
This object gives specific change information about a collection.
*/
public enum CollectionChangeInformation: Equatable {
/// This indicates that an element was updated at a specific index.
case update(index: Int)
/// This indicates that an element was deleted at a specific index.
case delete(index: Int)
/// This indicates that an element was inserted at a specific index.
case insert(index: Int)
}
public func ==(lhs: CollectionChangeInformation, rhs: CollectionChangeInformation) -> Bool {
switch (lhs, rhs) {
case (.update(let l), .update(let r)):
return l == r
case (.delete(let l), .delete(let r)):
return l == r
case (.insert(let l), .insert(let r)):
return l == r
default:
return false
}
}惊不惊喜,意外不?在枚举的枚举值里update发现了参数这是associated values,你可以理解为这些参数保存在了枚举的变量里面(You can think of the associated values as behaving like stored properties of the enumeration case instance),而且还遵守了Equatable协议,意味着可以自己定义怎么判断两个枚举值是否相等。来看看在苹果官方sdk中说了啥
/// extension StreetAddress: Equatable {
/// static func == (lhs: StreetAddress, rhs: StreetAddress) -> Bool {
/// return
/// lhs.number == rhs.number &&
/// lhs.street == rhs.street &&
/// lhs.unit == rhs.unit
/// }
/// }
public protocol Equatable {
/// Returns a Boolean value indicating whether two values are equal.
///
/// Equality is the inverse of inequality. For any values `a` and `b`,
/// `a == b` implies that `a != b` is `false`.
///
/// - Parameters:
/// - lhs: A value to compare.
/// - rhs: Another value to compare.
public static func ==(lhs: Self, rhs: Self) -> Bool
}
extension Equatable {
/// Returns a Boolean value indicating whether two values are not equal.
///
/// Inequality is the inverse of equality. For any values `a` and `b`, `a != b`
/// implies that `a == b` is `false`.
///
/// This is the default implementation of the not-equal-to operator (`!=`)
/// for any type that conforms to `Equatable`.
///
/// - Parameters:
/// - lhs: A value to compare.
/// - rhs: Another value to compare.
public static func !=(lhs: Self, rhs: Self) -> Bool
}Functional Reactive Programming(以下简称FRP)是一种响应变化的编程范式
我们之前一直在使用ReactiveCocoa 【ReactiveCocoa (RAC) is a Cocoa framework inspired by Functional Reactive Programming】,这两天又接触了RxSwift、RxCocoa,发现他们很类似,各有所长。之所以在这里说是因为看到RxCocoa在UI方面更加强大
/**
Binds sequences of elements to collection view items.
- parameter cellIdentifier: Identifier used to dequeue cells.
- parameter source: Observable sequence of items.
- parameter configureCell: Transform between sequence elements and view cells.
- parameter cellType: Type of table view cell.
- returns: Disposable object that can be used to unbind.
Example
let items = Observable.just([
1,
2,
3
])
items
.bind(to: collectionView.rx.items(cellIdentifier: "Cell", cellType: NumberCell.self)) { (row, element, cell) in
cell.value?.text = "\(element) @ \(row)"
}
.disposed(by: disposeBag)
collectionView.rx.itemSelected.subscribe({ [weak self] indexPath in
// do something
}).disposed(by: disposeBag)
*/有没有很酷,哈哈 看起来不错哦上面例子中只是列举了最简单的一种看下面的复杂的
/**
Binds sequences of elements to collection view items using a custom reactive data used to perform the transformation.
- parameter dataSource: Data source used to transform elements to view cells.
- parameter source: Observable sequence of items.
- returns: Disposable object that can be used to unbind.
Example
let dataSource = RxCollectionViewSectionedReloadDataSource<SectionModel<String, Double>>()
let items = Observable.just([
SectionModel(model: "First section", items: [
1.0,
2.0,
3.0
]),
SectionModel(model: "Second section", items: [
1.0,
2.0,
3.0
]),
SectionModel(model: "Third section", items: [
1.0,
2.0,
3.0
])
])
dataSource.configureCell = { (dataSource, cv, indexPath, element) in
let cell = cv.dequeueReusableCell(withReuseIdentifier: "Cell", for: indexPath) as! NumberCell
cell.value?.text = "\(element) @ row \(indexPath.row)"
return cell
}
items
.bind(to: collectionView.rx.items(dataSource: dataSource))
.disposed(by: disposeBag)
*/MVVM
关于MVVM的介绍ReactiveViewModel,目前我们项目采用以下设计
model :仅仅是数据模型
view :这里的view包含所有的view和viewcontroller,其中view(包含cell和自定义view)仅仅是view,不包含任何model,另外viewcontroller仅仅负责Layout、Animations、Device rotation、View and window transitions、Presenting loaded UI
viewModel:所有的viewmodel会被viewcontroller持有,这里面负责处理页数调用PXApiMannager获取数据,并且保存在ViewModel的property里面,如果需要为cell准备数据,在这里进行加工
完整数据获取及刷新流程如下:
viewController(订阅ViewModel的某个Signal,如果有输出数据刷新view,如果有错误提示错误)——————>viewModel(调用PXApiManager获取某个signal,进行map加工操作,将数据自身持有)—————>PXApiManager(创建signal,并且调用AFNetworking获取相应数据,如果有有数据则通过Mantle转化为model并向创建的signal抛出,如果有错误也抛出,这里也会进行接口异常记录,链接请求统一处理header,统一添加token信息等等)
IGListKit
IGListKit是Facebook的又一神作,这里是raywenderlich上的一篇教程,教你如何快速的在list中添加功能,而且滑动起来非常的流畅。IGListKit非常智能,会自动检查你数据中的变化,并流畅的更新UICollectionView 中对应改变数据的部分。
总体分为五步:
1、声明一个IGListCollectionView的变量,并且添加到当前viewcontroller当中,并且设置布局
// 1
let collectionView: IGListCollectionView = {
// 2
let view = IGListCollectionView(frame: CGRect.zero, collectionViewLayout: UICollectionViewFlowLayout())
// 3
view.backgroundColor = UIColor.black
return view
}()2、声明一个IGListAdapter的变量,并且为之设置view和databsource
lazy var adapter: IGListAdapter = {
return IGListAdapter(updater: IGListAdapterUpdater(), viewController: self, workingRangeSize: 0)
}()
adapter.collectionView = collectionView
adapter.dataSource = self3、在datasource中设置数据、IGListSectionController及为空时显示的view,注意⚠️这里的IGListSectionController相当于上面我们提到的ViewModel,你可以在里面控制列表中的单元如何显示
// MARK: - IGListAdapterDataSource
extension FeedViewController: IGListAdapterDataSource {
func objects(for listAdapter: IGListAdapter) -> [IGListDiffable] {
var items: [IGListDiffable] = [wxScanner.currentWeather]
items += loader.entries as [IGListDiffable]
items += pathfinder.messages as [IGListDiffable]
return items.sorted(by: { (left: Any, right: Any) -> Bool in
if let left = left as? DateSortable, let right = right as? DateSortable {
return left.date > right.date
}
return false
})
}
func listAdapter(_ listAdapter: IGListAdapter, sectionControllerFor object: Any) -> IGListSectionController {
if object is Message {
return MessageSectionController()
} else if object is Weather {
return WeatherSectionController()
} else {
return JournalSectionController()
}
}
func emptyView(for listAdapter: IGListAdapter) -> UIView? { return nil }
}4、在IGListSectionController里面设置边距、Section里面有几个单元cell、每个cell又用的哪种类型,并用model填充cell
import IGListKit
class MessageSectionController: IGListSectionController {
var message: Message!
override init() {
super.init()
inset = UIEdgeInsets(top: 0, left: 0, bottom: 15, right: 0)
}
}
// MARK: - IGListSectionType
extension MessageSectionController: IGListSectionType {
func numberOfItems() -> Int {
return 1
}
func sizeForItem(at index: Int) -> CGSize {
guard let context = collectionContext else { return .zero }
return MessageCell.cellSize(width: context.containerSize.width, text: message.text)
}
func cellForItem(at index: Int) -> UICollectionViewCell {
let cell = collectionContext?.dequeueReusableCell(of: MessageCell.self, for: self, at: index) as! MessageCell
cell.messageLabel.text = message.text
cell.titleLabel.text = message.user.name.uppercased()
return cell
}
func didUpdate(to object: Any) {
message = object as? Message
}
func didSelectItem(at index: Int) {}
}5、当你的数据有更新时,你需要执行
adapter.performUpdates(animated: true)但是看起来并没有Rxswift那么简单有没有,但是性能应该是没问题的。具体可以测试一下。